Golf courses aren’t just manicured landscapes; they’re carefully cultivated ecosystems where the type of grass plays a pivotal role in the game. The grass underfoot affects everything from the ball’s lie to the speed of the greens. Let’s delve into the world of turf grasses and uncover grass types used on golf courses.
Why Does Grass Types Used on Golf Courses Matter?
Different grasses offer unique playing characteristics:
- Ball Speed: Some grasses create smooth surfaces for fast-rolling putts, while others are slower and more forgiving.
- Resilience: Certain grasses can withstand heavy foot traffic and diverse weather conditions better than others.
- Aesthetics: The color, texture, and density of the grass contribute to the course’s visual appeal like tennis.
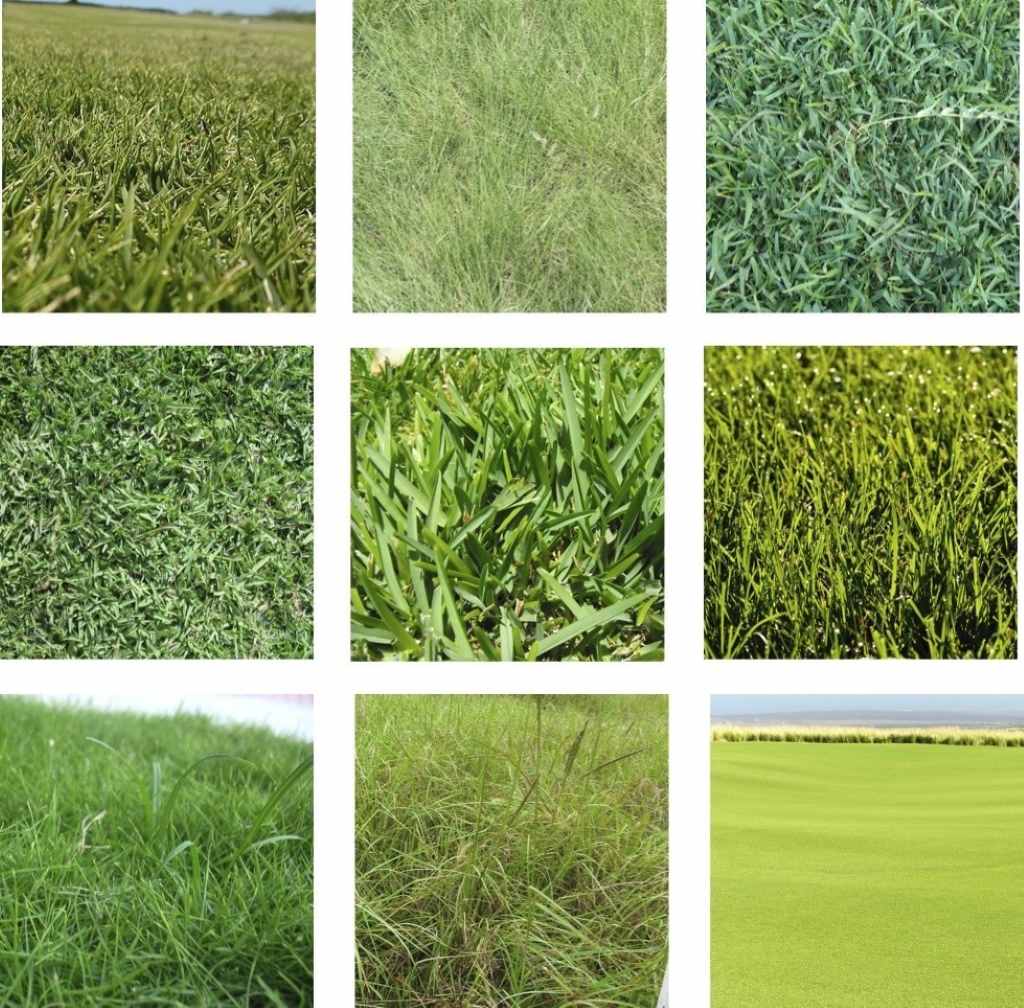

Major Types of Golf Course Grasses
1. Bentgrass:
- Characteristics: Fine-bladed, dense, and creates a smooth putting surface. Prefers cool, humid climates.
- Used For: Primarily greens (putting surfaces) due to its ability to be cut very low. Some fairways (especially in cooler regions).
- Varieties: Creeping bentgrass, Colonial bentgrass
- Pros: Excellent for fast greens, high aesthetic appeal
- Cons: Requires intensive maintenance, susceptible to some diseases
2. Bermuda Grass:
- Characteristics: Warm-season grass, aggressive grower, can tolerate heat and drought.
- Used For: Greens in warmer climates, fairways, tees.
- Varieties: TifEagle, Tifdwarf, Champion
- Pros: Durable, handles wear well, versatile
- Cons: Can be grainier, not as smooth for putting as bentgrass
3. Zoysia Grass:
- Characteristics: Warm-season, dense, wear-tolerant, drought-resistant.
- Used For: Tees, fairways (becoming more popular for greens in some regions)
- Varieties: Emerald, Zeon
- Pros: Low maintenance, good in transition zones
- Cons: Can have a stiffer feel, slower green speeds than bentgrass or Bermuda
4. Fescue:
- Characteristics: Cool-season, bunch-type growth, drought-tolerant, can handle shade.
- Used For: Roughs, fairways (especially on links courses), some greens
- Varieties: Tall fescue, Fine fescue (Chewings, creeping red)
- Pros: Low-maintenance, visually interesting, adaptable
- Cons: Can be clumpy if not managed properly
5. Ryegrass (Perennial and Annual):
- Characteristics: Cool-season, fast germination, used for overseeding dormant warm-season grasses in winter.
- Used For: Overseeding fairways and roughs
- Pros: Provides year-round color
- Cons: Can be a different texture/color than the base grass
Grass Selection: It’s All About Location
The choice of grass is heavily influenced by the course’s geographical location and climate.
- Cool-Season Zones: (Northern US, Canada, UK) Bentgrass, Fescue, Ryegrass
- Warm-Season Zones: (Southern US, Australia) Bermuda, Zoysia, some warm-season bentgrass
- Transition Zones: (Mid-Atlantic, Upper South) A mix of both cool and warm-season grasses
Beyond the Basics: The Golf Course Ecosystem
The type of grass is just one piece of the puzzle. Soil conditions, maintenance practices, water availability, and even sunlight exposure all contribute to a golf ball’s playing characteristics. Course superintendents carefully manage these factors to ensure optimal playing conditions throughout the year.
For the Golf Enthusiast: What to Look For
Next time you’re on a course, pay attention to the grass. Notice the difference between the fairway and the green. Does the ball sit up nicely on the tee? How does it roll on the putting surface? Understanding the role of grass types used on golf courses can deepen your appreciation for the game and even help you strategize your shots.